Here is the link.
Third practice - C# play with bit manipulation solution
Oct. 29, 2020
698. Partition to K Equal Sum Subsets
It is my 30 minutes learning to write a C# solution to apply bit manipulation. I like to learn the design using a simple test case with the array [1, 2, 3, 4] and k = 2.
Case study
I have to go through the debugging using [1, 2, 3, 4] in order for me to understand the code. But somehow I still am not sure why return dp[n - 1].
size = 2^ 4 = 26
dp[0] = true;
total = new int[16];
In order to save subset sum, let us go over the example,
each number in the array take ith bit as 1.
{1}, first number in the array, take first bit, bit expression: 1 -> integer 1, total[1] = 1, dp[1] = true;
{2}, second number in the array, take second bit, bit expression: 10 -> integer 2, total[2] = 2, dp[2] = true;
{3}, third number in the array, take third bit, bit expression: 100 -> integer 4, total[3] = 3, dp[3] = true;
{4}, fourth number in the array, take fourth bit, bit expression: 1000 -> integer 8, total[8] = 4, dp[8] = true;
if(dp[i]) // in other words, there is a subset in binary format, we can tell what subset it is.
dp[5] - 5 can tell the subset {1, 3}, first bit and third bit is found in 5 { binary format: 101}
Debug result: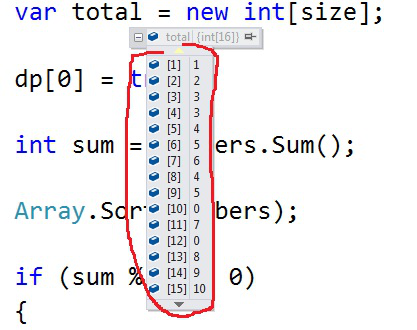
For example, total[6] = 5, subset {2, 3}, total is 5, bit expression for those numbers are 110.
dp[5] = true, in other words, there is a subset to match 5, {2, 3}.
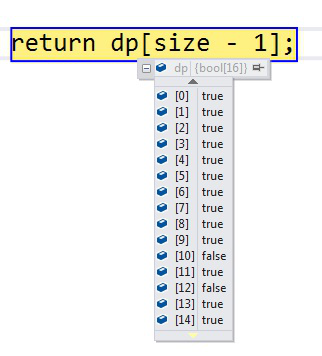
How to understand dp[10] = false, dp[12] = false?
10 -> 1010 -> subset {2, 4}, sum = 6 > 5, so it is not selected. dp[10] = false;
12 -> 1100 -> subset {3, 4}, sum= 7 > 5, sp it is not selected. dp[12] = false;
Advice
It is better for me to go over a simple test case, so that I can learn from my experience. It should be easy for me to come out design next time.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _698_partition_k_subset___bit
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var numbers = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
var result = CanPartitionKSubsets(numbers, 2);
}
/// <summary>
/// Oct. 29, 2020
/// study code
/// https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-to-k-equal-sum-subsets/discuss/335668/DP-with-Bit-Masking-Solution-%3A-Best-for-Interviews
/// </summary>
/// <param name="numbers"></param>
/// <param name="k"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool CanPartitionKSubsets(int[] numbers, int k)
{
if (numbers == null || numbers.Length == 0)
{
return false;
}
int n = numbers.Length;
var size = 1 << n;
// quick warmup:
// set A {1,2,3,4,5}
// the bitmask 01010 represents the subset {2,4}
// set ith bit:
// Let i=0, so, (1<<i) = 00001, 01010 | 00001 = 01011
// unset ith bit:
// b & !(1<<i)
// make sure that I understand the above tutorial before I continue to read the code
var dp = new bool[size];
var total = new int[size];
dp[0] = true;
int sum = numbers.Sum();
Array.Sort(numbers);
if (sum % k != 0)
{
return false;
}
// continue to use same variable sum -> 1 of k share
sum /= k;
if (numbers[n - 1] > sum)
{
return false;
}
// Loop over power set
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if(dp[i])
{
// Loop over each element to find subset
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// set the jth bit - add jth number in the subset
int temp = i | (1 << j);
var unvisited = temp != i;
if (unvisited)
{
var current = total[i];
var jth = numbers[j];
// if total sum is less than target store in dp and total array
if (jth <= (sum - (current % sum)))
{
dp[temp] = true;
total[temp] = jth + current;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return dp[size - 1];
}
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment